HERNIA
A hernia is a condition that occurs when an internal organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or tissue. It can occur in various parts of the body, but it most commonly affects the abdomen.
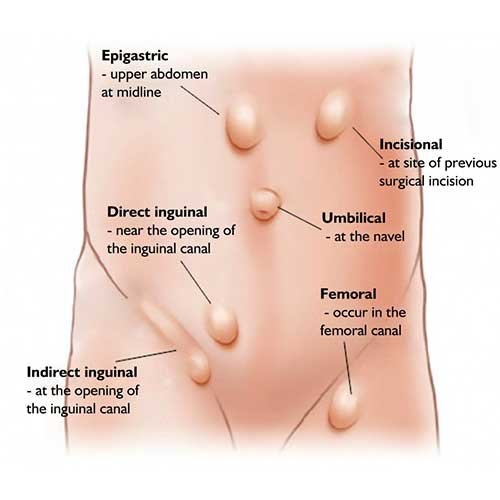
Types of Hernias
There are several types of hernias, including:
1. Inguinal hernia: This is the most common type of hernia and occurs when part of the intestine or abdominal tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles in the groin area.
2. Femoral hernia: This type of hernia occurs when part of the intestine or abdominal tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles near the upper thigh.
3. Umbilical hernia: This occurs when part of the intestine or abdominal tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles around the navel.
4. Incisional hernia: This type of hernia occurs when the intestine or abdominal tissue protrudes through a weakened area in the abdominal muscles at the site of a previous surgery.
5. Hiatal hernia: This occurs when part of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity.
6. Epigastric hernia: This occurs when part of the intestine or abdominal tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles in the upper abdomen, between the belly button and the breastbone.
7. Spigelian hernia: This is a rare type of hernia that occurs when part of the intestine or abdominal tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles along the edge of the rectus abdominis muscle.
Symptoms of Hernia
The symptoms of a hernia may vary depending on the type and location of the hernia. However, some common symptoms of a hernia include:
- A visible bulge or lump in the affected area, which may be more noticeable when coughing, sneezing, or straining.
- Pain or discomfort in the affected area, which may worsen with activity or when lifting heavy objects.
- A feeling of heaviness or pressure in the affected area.
- Nausea, vomiting, or constipation, especially if the hernia is affecting the digestive system.
- A burning or aching sensation at the site of the hernia.
- Difficulty swallowing or heartburn, if the hernia is a hiatal hernia affecting the upper stomach.
- Weakness, fatigue, or a general feeling of discomfort.
If left untreated, a hernia can cause complications, such as bowel obstruction, strangulation, or a loss of blood supply to the affected tissue, which can be life-threatening. If you experience any of the above symptoms, it is important to see a doctor for an evaluation and proper diagnosis.
Treatment Options For Hernia
The treatment of a hernia typically depends on the type and severity of the hernia. In many cases, surgery is the most effective treatment option for a hernia, especially if the hernia is causing symptoms or complications. However, some small hernias that are not causing any symptoms may not require treatment and can be monitored closely by a doctor.
Types of Hernia Surgeries
There are several types of hernia surgeries that may be performed, depending on the location and severity of the hernia. Some common types of hernia surgeries include:
- Open hernia repair: In this type of surgery, an incision is made near the hernia, and the protruding tissue is pushed back into the abdominal cavity. The weakened area in the abdominal wall is then reinforced with stitches or a mesh patch.
- Laparoscopic hernia repair: This type of surgery is performed using a laparoscope, which is a thin tube with a camera and light on the end. Several small incisions are made, and the laparoscope and surgical instruments are inserted through the incisions. The hernia is repaired using a mesh patch, which is inserted through one of the incisions.
Recurrence of Hernia
Unfortunately, hernias can sometimes recur after surgery. The risk of recurrence depends on several factors, including the type and location of the hernia, the technique used during surgery, and the patient’s overall health.
Some factors that can increase the risk of hernia recurrence include:
- Straining: Activities that put strain on the abdominal muscles, such as heavy lifting, can increase the risk of hernia recurrence. It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions regarding activity levels after surgery.
- Infection: Infections at the surgical site can increase the risk of hernia recurrence. Proper wound care and infection prevention measures can help reduce this risk.
- Smoking: Smoking can interfere with the healing process and increase the risk of complications, including hernia recurrence.
- Obesity: Excess weight can put added strain on the abdominal muscles and increase the risk of hernia recurrence.
If a hernia does recur, further surgery may be necessary to repair it. However, the risk of recurrence can often be minimized through proper surgical technique, postoperative care, and lifestyle modifications.
Have Questions? Get in touch!
Adjoining More Supermarket,
Jalandhar 144022

